Ever wondered how electric cars are so efficient compared to gas cars? It’s all about their power systems. Electric vehicles (EVs) have a simple setup with a motor and a controller. This makes them better for the environment and gives a smoother ride. We’ll look into what makes EV engines special and how they’re changing the way we travel.
From the tech behind EV engines to how they’re changing the game, we’ll cover it all. Let’s dive into the world of electric vehicle engines and see why they’re the future of driving.
Key Takeaways
- Electric vehicles can travel between 50 to over 500 miles on a single charge.
- Regenerative braking technology enhances EV efficiency and reduces wear on brake components.
- Compared to internal combustion engines, EVs boast an efficiency rating of over 77%.
- Modern BEVs can often recharge overnight, offering convenience for users.
- EV power systems require significantly fewer moving parts, leading to less maintenance.
Understanding Electric Vehicle Power Systems
The world of cars is changing fast, with electric vehicles (EVs) becoming more popular. Learning about the components of an EV power system shows how advanced these cars are. Unlike old cars with gas engines, EVs use new tech for better performance and less waste.
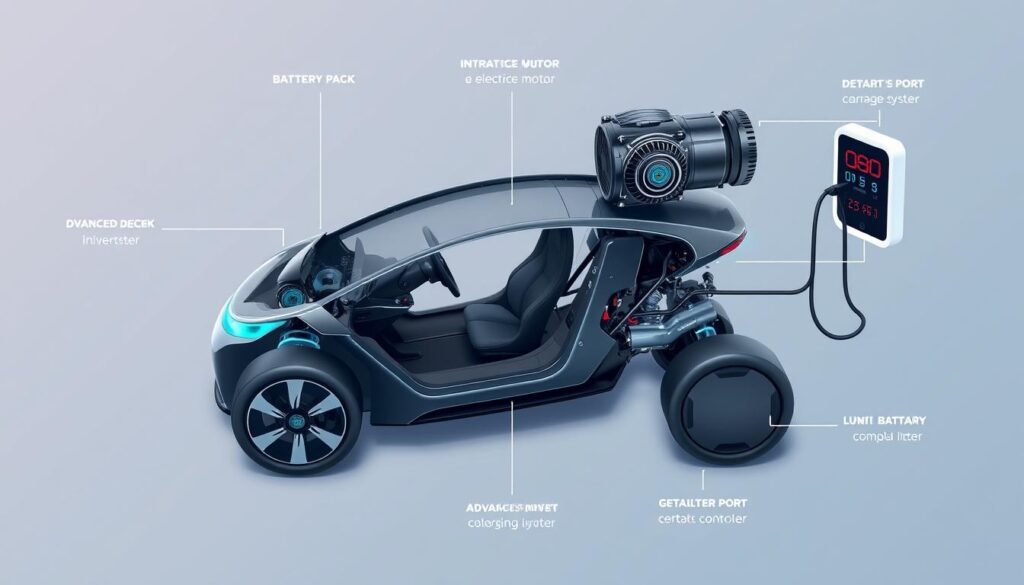
Components of an EV Power System
The main نظام الدفع الكهربائي has three key parts:
- Electric Traction Motor: This part moves the car, using power from the battery. It’s also good at making power back when you brake.
- Battery Pack: Usually made of lithium-ion, it holds the energy needed to move the car. The type of battery affects how heavy the car is and how far it can go.
- Controller: This is the brain of the system. It sends power and changes DC to AC for cars with AC motors. It controls speed and helps with braking.

Comparison with Traditional Gasoline-Powered Vehicles
Electric cars are very different from old cars with gas engines. Both want to move the car, but they do it in different ways. Gas engines use only 17-21% of their energy to move the car, while EVs use 85-90%.
Some EVs can go as fast as 470hp, much faster than the 120hp of most old cars. The electric motor makes EVs go up to 250 miles on one charge. It takes 4-10 hours to fully charge an EV with a Level 2 charger.
Even though EVs cost more at first, they save money on upkeep and get up to $7,500 in tax credits. They also use less energy than gas cars, turning over 77% of battery energy into power for the wheels.
| Component | Electric Vehicles | Gasoline-Powered Vehicles |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Conversion Efficiency | 77% – 90% | 12% – 30% |
| Average Horsepower | Up to 470hp | 120hp |
| Range on Full Charge/Tank | Up to 250 miles | Varies |
| Charging Time | 4-10 hours | N/A |
Types of Electric Motors in Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles use different motors to improve efficiency and performance. It’s important to know the differences between Direct Current (DC) Motors and Alternating Current (AC) Motors. Each type has its own strengths for electric vehicles.
Direct Current (DC) Motors
DC Motors, especially brushless ones, are popular for their reliability and long life. They work by magnetic forces in coils, making them good at low speeds. But, they have lower efficiency and need more maintenance, which limits their use in EVs.
Alternating Current (AC) Motors
AC Motors are becoming more common in electric vehicles. They are more efficient and need less maintenance than DC Motors. Three-phase induction motors and Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) are especially good for EVs. They handle power well and are efficient, making them key for hybrid electric cars.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Motor Type
Each motor type has its own benefits and drawbacks:
| Motor Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Current (DC) Motors | Simplicity in control systemsLower initial costsHigh torque at low speeds | Lower overall efficiencyMaintenance challengesHeavier weight |
| Alternating Current (AC) Motors | Higher efficiency (up to 95%)Less maintenance requiredLonger lifecycle | Higher initial costs due to electronicsMore complex control systems |
Electric Vehicle Engines and Their Performance
Electric vehicle (EV) engines boost performance with new tech and designs. They show how electric motors, batteries, and regenerative systems change our roads.
Kinetic Energy Recovery: Regenerative Braking
Kinetic Energy Recovery: Regenerative Braking is key in EVs today. It turns deceleration energy into electrical energy. This energy recharges the battery, adding 5-10% to the driving range.
This tech also means less brake wear. So, it cuts down on maintenance costs over time. The smooth use of this system makes EVs more efficient and green.
Efficiency Ratings of Electric Motors
The Efficiency Ratings of Electric Motors show how well EVs perform. Electric motors turn over 85% of electrical energy into motion. This is much better than gas engines, which use less than 40%.
Electric engines use 59-62% of grid energy for movement. This means they use less energy and last longer. It’s a big win for electric vehicles.
Battery Technologies: Lithium-Ion vs. Other Types
Battery Technologies, especially Lithium-Ion vs. Other Types, are crucial for EVs. Lithium-ion batteries lead because of their high energy and long life. Other types, like nickel-metal hydride or lead-acid, don’t match up well.
Looking at battery tech, lithium-ion is the top choice. It offers the best performance for today’s EVs.

Exploring Advanced EV Power Technologies
Electric vehicles are leading a technological change. They are powered by new power technologies. Smart Controllers are key to making electric vehicles better and more efficient.
These devices use smart algorithms to control energy use. They improve how electric systems work.
Smart Controllers and Their Functions
Smart Controllers are essential for electric vehicles. They enable features like regenerative braking and adjustable speed. This makes driving better and extends the vehicle’s range.
They work well with advanced electric systems. This helps in making transportation more sustainable.
The Role of Power Electronics in EVs
Power Electronics are crucial for EVs. They make sure energy moves smoothly from the battery to the motor. This boosts motor performance and helps in capturing energy back.
A good power electronics system is the base for efficient electric systems.
Emerging Trends in Electric Vehicle Engineering
The EV industry is changing fast. New things like solid-state batteries and in-wheel motors are coming. They make EVs more efficient and powerful.
Designs are also getting better. They use new materials and designs for longer battery life and faster charging. This move towards sustainability improves vehicle performance and helps the environment.
Conclusion
The car industry is moving towards electric vehicles and green transport. Knowing how these cars work is key. Electric cars make up just 14% of all car sales worldwide.
But, they’re crucial for cutting down on emissions. The transport sector uses over 25% of the world’s energy and causes a lot of pollution. So, making electric cars better is very important.
Better batteries, more charging spots, and smart tech are changing transport. In Europe, electric car sales have grown a lot since 2010. This shows a big push towards cleaner cars everywhere.
Electric cars can be up to 40% cleaner than gas cars. This makes them a big step towards a greener future. But, there are still hurdles like battery tech and charging spots.
More money and support from governments can help fix these issues. Moving to electric cars is a big step towards being kinder to our planet. It makes transport more efficient too.
By learning about electric car power systems, we see their value. They help us work together for a cleaner world.
FAQ
What are the main components of an electric vehicle’s power system?
An electric vehicle’s power system includes the Electric Traction Motor, Battery Pack, and Controller. The motor drives the wheels using energy from the battery pack. The controller manages power and performance.
How do electric vehicles compare to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles?
Electric vehicles have a simpler system with an electric motor and controller. Gasoline vehicles have complex systems like engines and exhausts. This makes electric vehicles more efficient and cheaper to maintain.
What are the efficiency ratings of electric motors?
Electric motors are very efficient. AC motors can reach up to 95% efficiency. DC motors are between 85% and 95%. This means they use less energy and last longer.
What is regenerative braking and how does it work?
Regenerative braking turns deceleration into electricity, recharging the battery. It improves range by 5-10% and reduces brake wear. This saves money on maintenance over time.
What types of batteries are commonly used in electric vehicles?
Lithium-ion batteries are the most used in electric vehicles. They have high energy density and last long. They are preferred over other types like nickel-metal hydride or lead-acid.
How do smart controllers enhance electric vehicle performance?
Smart controllers use advanced algorithms to optimize energy use and extend range. They manage performance and enhance driving experience through regenerative braking and variable speed.
What is the role of power electronics in electric vehicles?
Power electronics manage energy flow between the battery, motor, and other parts. They ensure efficient motor operation and channel excess energy back into the battery during regeneration.
What are current trends in electric vehicle technology?
Trends include solid-state batteries, better charging, automation, and advanced power electronics. These aim to boost efficiency, performance, and sustainability in electric vehicles.